Product & Service

【Name of drug】
Common name: Glucose Injection
Product name: Glucose Injection
【Ingredients】
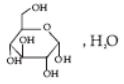 The main component of this product is glucose.
The main component of this product is glucose.
Chemical name: D-(+)-glucopyranose monohydrate.
Structural formula:
Molecular formula: C 6 H 12 O 6 ·H 2 O
Molecular weight: 198.17
【Properties】
This product is a colorless or almost colorless clear liquid; sweet.
【Indications】
(1) supplement energy and body fluid; used for various reasons such as insufficient eating or loss of body fluids (such as vomiting, diarrhea, etc.), total intravenous nutrition, hunger ketosis; (2) hypoglycemia; (3) high Potassiumemia; (4) hypertonic solution used as tissue dehydrating agent; (5) preparation of peritoneal dialysate; (6) drug diluent; (7) intravenous glucose tolerance test; (8) preparation of GIK (polarization solution) ) for liquid use.
【Specification】
(1) 50 ml: 2.5 g; (2) 100 ml: 5 g; (3) 250 ml: 12.5 g; (4) 500 ml: 25 g;
(5) 50 ml: 5 g; (6) 100 ml: 10 g; (7) 250 ml: 25 g; (8) 500 ml: 50 g.
【Adverse reactions】
(1) Phlebitis occurs when infusion of hypertonic Glucose Injection. If a large intravenous drip is used, the incidence of phlebitis decreases.
(2) high concentration of Glucose Injection extravasation can cause local swelling and pain.
(3) Reactive hypoglycemia: a combination of excessive insulin use, the original tendency of hypoglycemia and the sudden stop of total intravenous nutrition therapy are prone to occur.
(4) hyperglycemia non-ketotic coma: more common in diabetes, stress, the use of a large number of glucocorticoids, uremia peritoneal dialysis patients intraperitoneal administration of hypertonic glucose solution and total nutrition therapy.
(5) Electrolyte disorder, low potassium, low sodium and hypophosphatemia are prone to occur when glucose is directly supplied for a long time.
(6) The original heart function is incomplete.
(7) Hyperkalemia, occasionally occurs in patients with type I diabetes with high concentrations of glucose.
[taboo]
(1) those who are not controlled by diabetic ketoacidosis;
(2) hyperglycemia non-ketotic hyperosmolar state.
【Precautions】
(1) Pay attention to excessive glucose during childbirth to stimulate fetal insulin secretion, and hypoglycemia in infants after birth.
(2) The following conditions should be used with caution: 1 Most patients with gastric resection are prone to dumping syndrome and hypoglycemia when taking oral glucose tolerance test. They should be changed to intravenous glucose test: 2 patients with periodic paralysis and hypokalemia; Excitatory state or the application of glucocorticoids can easily induce hyperglycemia; 4 edema and severe heart, renal insufficiency, cirrhosis of ascites, easy to cause water retention, should control the amount of infusion; cardiac dysfunction should especially control the drip rate.
【Pregnant women and lactating women】
Injecting too much glucose during childbirth can stimulate fetal insulin secretion and produce hypoglycemia in infants after birth.
【Children's medication】
Rehydration too fast, too much, can cause heart palpitations, arrhythmia, and even acute left heart failure.
【Geriatric Use】
Rehydration too fast, too much, can cause heart palpitations, arrhythmia, and even acute left heart failure.
【Drug Interactions】This experiment was not performed and there is no reliable reference.
【Drug overdose】 This experiment was not performed and there is no reliable reference.
【Pharmacology and Toxicology】
Glucose is one of the main sources of heat in the body. It produces 4 calories (16.7 kJ) of heat per gram of glucose and is used to supplement calories. Treatment of hypoglycemia. When glucose and insulin are intravenously infused together, the synthesis of glycogen requires potassium ions to participate, so that potassium ions enter the cell and the blood potassium concentration decreases, so it is used to treat hyperkalemia. Hypertonic Glucose Injection Rapid decompression of tissue dehydration can be used as a tissue dehydrating agent. In addition, glucose is the main substance that maintains and regulates the osmotic pressure of peritoneal dialysate.
【Pharmacokinetics】
Intravenous glucose directly enters the blood circulation. Glucose is completely oxidized in the body to produce CO 2 and water, which is excreted through the lungs and kidneys while producing energy. It can also be converted into glycogen and fat storage. Generally, the normal human body's ability to utilize glucose per minute is 6 mg/kg.
【Storage】 Closed storage.
【Package】 Non-PVC soft bag [pull ring, easy to fold (double valve)]: 50ml / bag × 80 bags; 100ml / bag × 80 bags; 250ml / bag × 40 bags; 500ml / bag × 20 bags.
【Validity】 24 months.
【Executive Standards】 "Chinese Pharmacopoeia" 2015 Edition 2
【Approval number】
|
50ml: 2.5g Chinese medicine standard word H20113017 |
50ml: 5g Chinese medicine standard word H20113014 |
|
100ml: 5g Chinese medicine standard word H20045167 |
100ml: 10g Chinese medicine standard word H33022595 |
|
250ml: 12.5g Chinese medicine standard word H33022596 |
250ml: 25g Chinese medicine standard word H33021927 |
|
500ml: 25g Chinese medicine standard word H33021495 |
500ml: 50g Chinese medicine standard word H33021494 |
【Manufacturer】
Company Name: Zhejiang Kancheer Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Production address: Beijiang Industrial Zone, Geshan Town, Dongyang City, Zhejiang Province,China
Website: www.kancheer.com
Zip code: 322105
Tel: (0579) 86019696 86019610
Fax number: (0579) 86019611
